Abstract
Background: Relapsed or refractory (R/R) Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) remains a significant clinical problem. Recently checkpoint blockade therapy (CBT) has shown striking activity in this setting, but the complete response (CR) rate is modest. Patients who relapse after CBT have limited therapeutic options. A prior, retrospective study showed that after anti-PD-1 therapy the objective response rate to chemotherapy alone was 61% (Rossi et al 2017). We investigated the effect of treatment subsequent to CBT in a large international multicenter retrospective analysis.
Methods: Seventeen centers across the US and Canada are participating in this study to date. Medical records of each institution were queried to identify HL patients who received CBT and were subsequently treated with an additional line of therapy. The primary aim of this analysis was to determine the best response to post-CBT treatment in patients who discontinued CBT due to progression of disease (PD), preparation for stem cell transplant (SCT), or toxicity. Patients who discontinued CBT due to CR, and patients whose best response could not be determined due to death from another cause were excluded from analysis. Responses were assessed using Lugano criteria. Survival status was analyzed for the entire study population and stratified by post-CBT treatment regimen and disease subgroups using the Kaplan-Meier method. Progression free survival (PFS) was calculated for patients with at least stable disease (SD) to post-CBT treatment. Log rank tests were performed to test for statistical significance. Two-sided P<0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
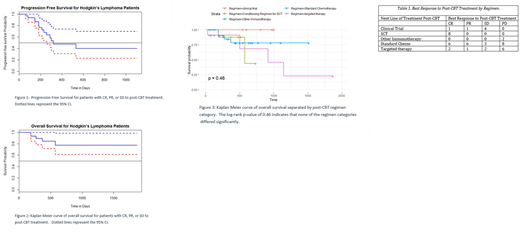
Results: To date, out of 121 total lymphoma patients, a total of 77 HL patients received a subsequent line of therapy after CBT. Their median age was 37 (range 23-74); there were 38 men and 39 women. Fifty of these patients met inclusion criteria. Of the included patients, 15 were stages 1-2 and 35 were stages 3-4. These patients were heavily pre-treated with a median of 4 prior therapies before CBT (range 1-10). Thirty-one patients received prior brentuximab vedotin (BV) and 28 patients had undergone allogeneic (3) or autologous (25) SCT. The median duration of response (DOR) to the line of therapy prior to CBT was 3.5 months; 18 (36%) patients had relapsed disease, and the remaining 32 (64%) had refractory disease prior to CBT. The best response to CBT included: 2 (4%) CR, 21 (42%) partial response (PR), 13 (26%) SD, 14 (28%) PD. Patients discontinued CBT due to PD (72%), preparation for transplant (16%), toxicity (8%), CR after the addition of chemotherapy (2%), and an infectious complication (2%). Post-CBT treatment regimens included standard chemotherapy (46%), targeted therapy (22%), conditioning regimens for SCT (16%), other immunotherapy (4%), or clinical trial drugs (12%). The objective response rate (ORR) for all patients to post-CBT treatment was 52%: 17 (34%) CR and 9 (18%) PR. Eight (16%) patients achieved SD, while 16 (32%) patients progressed. Overall response rate to post-CBT treatment correlated with response to CBT itself. Among patients with a CR or PR to CBT, their ORR to post-CBT treatment was 70%, whereas for non-responders to CBT the ORR to post-CBT treatment was 37%. At a median time of follow-up of 14 months, the median PFS for patients who achieved a CR, PR, or SD to post-CBT treatment (n=34) is 10.7 months (Figure 1). Twenty (58.8%) of these patients have not yet progressed, and the OS has not been reached (Figure 2), as 85% of patients remain alive. Currently there is no statistical difference in survival based upon post-CBT treatment received (Figure 3, Table 1). However, of note 21 patients received SCT subsequent to their post-CBT treatment: 8 allo and 13 auto. All of these patients remain alive, however, 9 of 12 (75%) have progressed post SCT.
Conclusions: In a heavily pretreated R/R HL population, treatment with CBT may sensitize patients to subsequent therapy, even after they progress on CBT. A response to CBT appears to correlate with response to post-CBT treatment, but PD to CBT did not preclude a response to subsequent therapy. Patient survival does not appear to be dependent upon the subsequent treatment regimen, although the majority of patients with at least stable disease went on to SCT. The long PFS in these patients is encouraging and may warrant further investigation. We plan to expand this analysis with additional patients prior to the December meeting.
Advani:Celgene: Research Funding; Roche/Genentech: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board, Research Funding; Kyowa: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board; Celgene: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Autolus: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board; Millenium: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Regeneron: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Kura: Research Funding; Agensys: Research Funding; Infinity: Research Funding; Cell Medica: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board; Merck: Research Funding; Bayer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board; Forty Seven Inc.: Research Funding; Gilead/Kite: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board, Research Funding. Herrera:AstraZeneca: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Merck, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Immune Design: Research Funding; KiTE Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding. Chen:Millennium Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech Inc.: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Affimed: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Merck & Co., Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Ramchandren:Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics LLC an AbbVie Company: Consultancy, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Merck: Research Funding. Assouline:BMS: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Wagner-Johnston:Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Merck: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; JUNO: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ASTEX: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding. Svoboda:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; KITE: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kyowa: Consultancy; Regeneron: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding. Barta:Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Merck, Takeda, Celgene, Seattle Genetics, Bayer: Research Funding. Karmali:Gilead: Speakers Bureau; AstraZeneca: Speakers Bureau. Persky:Morphosys (IDMC): Consultancy; Spectrum: Research Funding; Genentech: Honoraria; Merck: Research Funding. Smith:Portola: Honoraria; BMS: Consultancy. Diefenbach:Trillium: Research Funding; Denovo: Research Funding; Millenium/Takeda: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Merck: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.